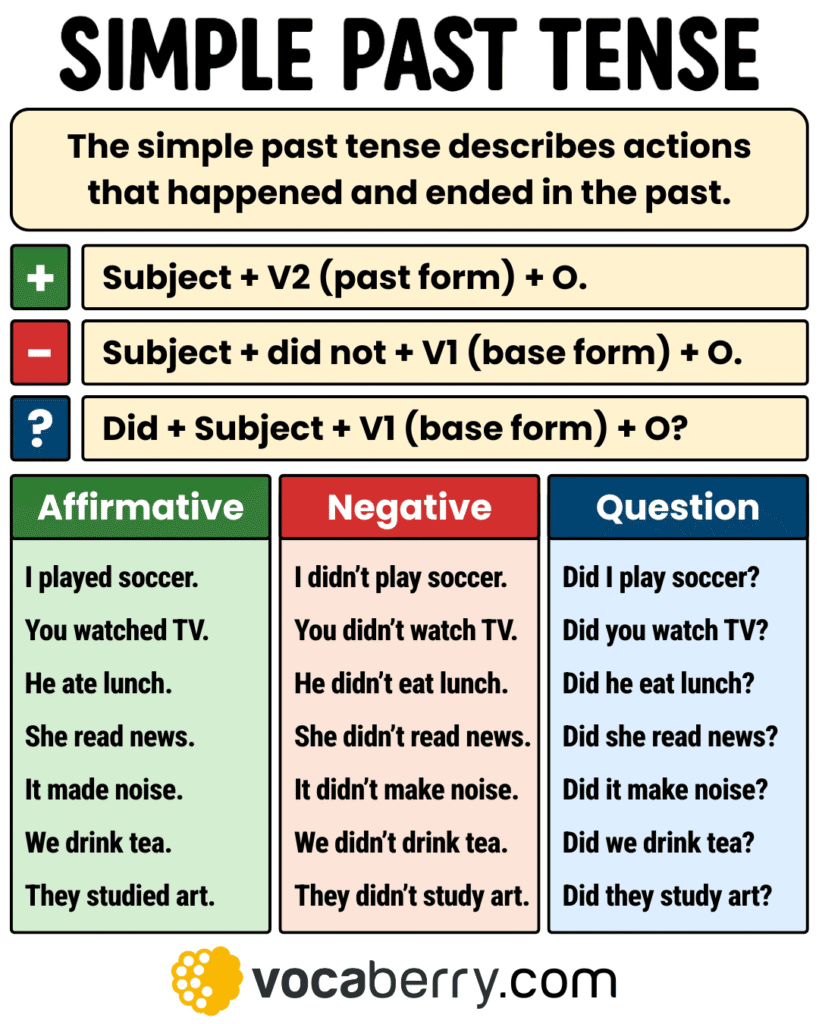
The simple past tense describes actions or situations that started and finished at a specific point in the past. It’s essential for narrating stories, reporting events, describing past habits, and expressing completed actions.
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to form and use the simple past tense in affirmative, negative, and question forms, understand its structure and usage, explore grammar rules, and work with regular and irregular verbs. You’ll also learn how to use common time expressions—all with clear examples.
When to Use the Simple Past Tense
The simple past is used to describe actions or situations that happened and finished in the past. It’s your go-to tense for telling stories, sharing experiences, and stating past facts. Here are the most essential uses:
1. Completed Actions in the Past
Used for actions that started and ended at a specific time in the past.
- I visited Rome last summer.
- She finished her report yesterday.
- They watched a documentary on TV last night.
2. Past Routines or Habits
Describes habits or routines that happened regularly in the past but no longer do.
- He jogged every morning when he lived in Boston.
- They played soccer every weekend in college.
- I studied French in high school.
3. A Series of Past Events
Used for listing events that occurred one after another in the past.
- I woke up, ate breakfast, and left for work.
- She entered the room, greeted everyone, and sat down.
- We finished lunch, cleaned up, and went out.
4. Historical Facts or Past Truths
States general truths or facts about the past.
- The Romans built roads across Europe.
- Dinosaurs lived millions of years ago.
- She was the top student in her class.
5. Past Events with a Clear Time Frame
Used when mentioning exactly when something happened.
- I moved to London in 2018.
- He graduated from university two years ago.
- They bought that house last month.
Simple Past Tense Structure
The simple past tense is formed by using the past form of the main verb. Regular verbs take -ed, while irregular verbs have unique forms. In negatives and questions, use did with the base verb. This tense is used to describe completed actions or situations in the past.
Affirmative Form
Use this form to talk about completed actions in the past. With regular verbs, add –ed; irregular verbs change form.
Structure: Subject + past form of verb
Examples:
- I visited my grandparents last weekend.
- She watched three episodes last night.
- They went to the concert yesterday.
Negative Form
Use this form to say that something did not happen in the past. Use did not (didn’t) + base verb.
Structure: Subject + didn’t + base verb
Examples:
- I didn’t finish my report on time.
- He didn’t go to the party.
- We didn’t see that movie yet.
Question Form
Use this form to ask whether an action happened. Begin with Did, then subject + base verb.
Structure: Did + subject + base verb?
Examples:
- Did you call the client yesterday?
- Did she arrive on time?
- Did they enjoy the trip?
Short Answers
In responses to yes/no questions, use short forms for simplicity.
Examples:
- Did you eat lunch? → Yes, I did. / No, I didn’t.
- Did he pass the test? → Yes, he did. / No, he didn’t.
- Did they finish on time? → Yes, they did. / No, they didn’t.
Summary Table: Simple Past Tense
| Type | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + past verb | She finished the project yesterday. |
| Negative | Subject + didn’t + base verb | We didn’t see her at the meeting. |
| Question | Did + subject + base verb? | Did you enjoy the concert? |
| Short Answer | Yes/No + subject + did/didn’t | Yes, I did. / No, we didn’t. |
Regular vs. Irregular Verbs – Simple Past Tense
In the simple past tense, the main verb changes depending on whether it is regular or irregular. This tense is used to describe completed actions that took place at a specific time in the past. There are two main types of verbs used in the simple past: regular verbs and irregular verbs.
Regular Verbs
Regular verbs form the simple past by adding -ed to the base form of the verb. If the verb ends in -e, just add -d. For verbs ending in a consonant + y, change the y to -ied.
| Base Verb | Past Simple | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| work | worked | She worked late last night. |
| play | played | We played soccer after school. |
| clean | cleaned | He cleaned his room yesterday. |
| call | called | I called my friend last weekend. |
| talk | talked | They talked about the plan. |
| study | studied | She studied hard for the exam. |
Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs do not follow a standard pattern. You must memorize their past tense forms because they don’t just take -ed. Many of the most commonly used verbs in English are irregular.
| Base Verb | Past Simple | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| go | went | She went to the mall yesterday. |
| eat | ate | I ate dinner at 7 p.m. last night. |
| write | wrote | He wrote a letter to his teacher. |
| see | saw | We saw a movie on Saturday. |
| take | took | They took the train to work. |
| buy | bought | I bought a new laptop last week. |
Time Expressions with the Simple Past Tense
Time expressions play an important role in the simple past tense. They help to clarify when an action happened in the past. These expressions often indicate a specific time, such as yesterday, last year, or in 2005. They make your sentences more complete and easier to understand.
Below are some of the most common time expressions used with the simple past tense:
| Time Expression | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| yesterday | I watched that movie yesterday. |
| last night | She cooked dinner last night. |
| last week | We visited our grandparents last week. |
| two days ago | He finished the project two days ago. |
| in 2010 | They got married in 2010. |
| on Monday | I met her on Monday. |
| this morning | He called me this morning. |
| a few minutes ago | She left the office a few minutes ago. |
| when I was a child | I lived in Paris when I was a child. |
| at 5 o’clock | The bus arrived at 5 o’clock. |






