When we talk about what someone else said, we can use reported speech (also called indirect speech). This means we do not repeat the exact words but rephrase them in our own way.
For example:
- Direct Speech: She said, “I love this book.”
- Reported Speech: She said she loved that book.
Learning reported speech is essential for everyday conversations, storytelling, and writing. In this article, we will explain how to change direct speech into reported speech, covering important grammar rules, verb tense changes, pronouns, time expressions, and common mistakes.
What Is Reported Speech?
Reported speech is used when we tell someone what another person said without repeating their exact words.
- Direct Speech: He said, “I am tired.”
- Reported Speech: He said he was tired.
Key difference:
- Direct speech uses quotation marks and repeats the exact words.
- Reported speech changes the tense, pronouns, and time expressions to fit the situation.
Rules for Changing Direct to Reported Speech
1. Change the Pronouns
When reporting speech, we need to change pronouns to match the perspective of the speaker.
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| He said, “I love my job.” | He said he loved his job. |
| She said, “This is my book.” | She said that was her book. |
| They said, “We enjoyed our trip.” | They said they had enjoyed their trip. |
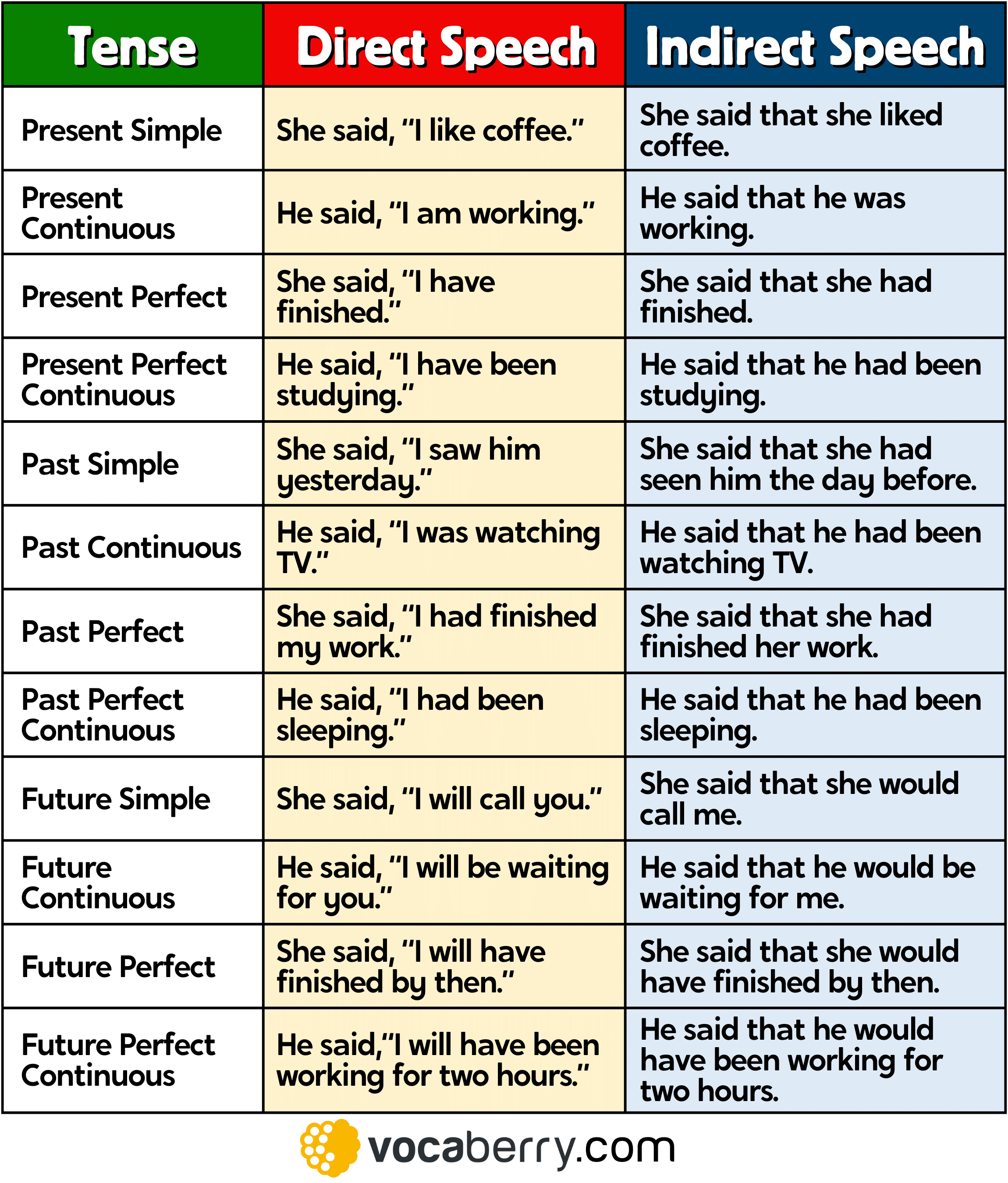
2. Change the Verb Tense
In reported speech, we usually move the verb one step back in time. This is called backshifting.
| Direct Speech (Present) | Reported Speech (Past) |
|---|---|
| “I am tired.” | He said he was tired. |
| “She likes coffee.” | He said she liked coffee. |
| “They are going to the park.” | She said they were going to the park. |
| Direct Speech (Past) | Reported Speech (Past Perfect) |
|---|---|
| “I went to London.” | He said he had gone to London. |
| “She bought a car.” | She said she had bought a car. |
| Direct Speech (Future) | Reported Speech (Would) |
|---|---|
| “I will call you.” | He said he would call me. |
| “She will visit us.” | She said she would visit them. |
Exception: If the reporting verb is in the present (e.g., He says…), we do not change the tense:
- He says, “I am tired.” → He says he is tired.
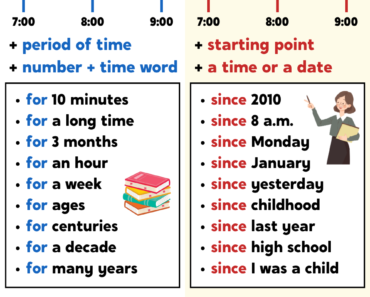
3. Change Time and Place Words
Time and place expressions often need to be adjusted in reported speech.
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| “I will do it tomorrow.” | He said he would do it the next day. |
| “She came yesterday.” | She said she had come the day before. |
| “We are meeting tonight.” | They said they were meeting that night. |
| “I saw her last week.” | He said he had seen her the previous week. |
| “I live here.” | He said he lived there. |
How to Report Different Types of Sentences
1. Reporting Statements
For statements, we use “said” or “told” (followed by a pronoun or object).
Direct: She said, “I like ice cream.”
Reported: She said she liked ice cream.
Direct: He told me, “You are late.”
Reported: He told me I was late.
2. Reporting Yes/No Questions
For yes/no questions, we use “asked if” or “asked whether” and change the sentence to statement form (no question marks).
Direct: He asked, “Are you coming?”
Reported: He asked if I was coming.
Direct: She asked, “Did he call?”
Reported: She asked whether he had called.
3. Reporting WH- Questions
For WH- questions (what, where, when, why, how, who), we use the WH-word and change the question into statement form.
Direct: He asked, “Where do you live?”
Reported: He asked where I lived.
Direct: She asked, “What are you doing?”
Reported: She asked what I was doing.
4. Reporting Commands and Requests
For commands and requests, we use “told” or “asked” + infinitive (to + verb).
Direct: She said, “Close the door!”
Reported: She told me to close the door.
Direct: He said, “Please help me.”
Reported: He asked me to help him.
For negative commands, we use “not to”.
Direct: She said, “Don’t touch that!”
Reported: She told me not to touch that.
Reported Speech Quiz – Test Your English
1. She said, “I am happy.” → She said she ___ happy.
a) is
b) was
c) has been
2. He said, “I will call you tomorrow.” → He said he ___ call me the next day.
a) will
b) would
c) can
3. They said, “We went to Paris last summer.” → They said they ___ to Paris the previous summer.
a) had gone
b) go
c) have gone
4. She said, “I can’t swim.” → She said she ___ swim.
a) couldn’t
b) can
c) cannot
5. He asked, “Did you see the movie?” → He asked if I ___ the movie.
a) see
b) saw
c) had seen
6. She asked, “Where do you live?” → She asked where I ___.
a) lived
b) live
c) living
7. “Let’s go to the park,” she said. → She suggested ___ to the park.
a) went
b) going
c) go
8. “Don’t be late,” he said. → He told me ___ late.
a) not to be
b) to be not
c) don’t be
9. He said, “I have finished my work.” → He said he ___ his work.
a) has finished
b) had finished
c) finishes
10. “What time is it?” she asked. → She asked what time it ___.
a) is
b) was
c) has been
Quiz Answers
1) was
2) would
3) had gone
4) couldn’t
5) had seen
6) lived
7) going
8) not to be
9) had finished
10) was