Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and object of a sentence are the same person or thing. They end in -self (singular) or -selves (plural), like myself or themselves. In this guide, you’ll learn what reflexive pronouns are, how to use them, their positions in sentences, the difference between reflexive and intensive pronouns, and see a complete list of reflexive pronouns with examples to help you use them confidently.
What Are Reflexive Pronouns?
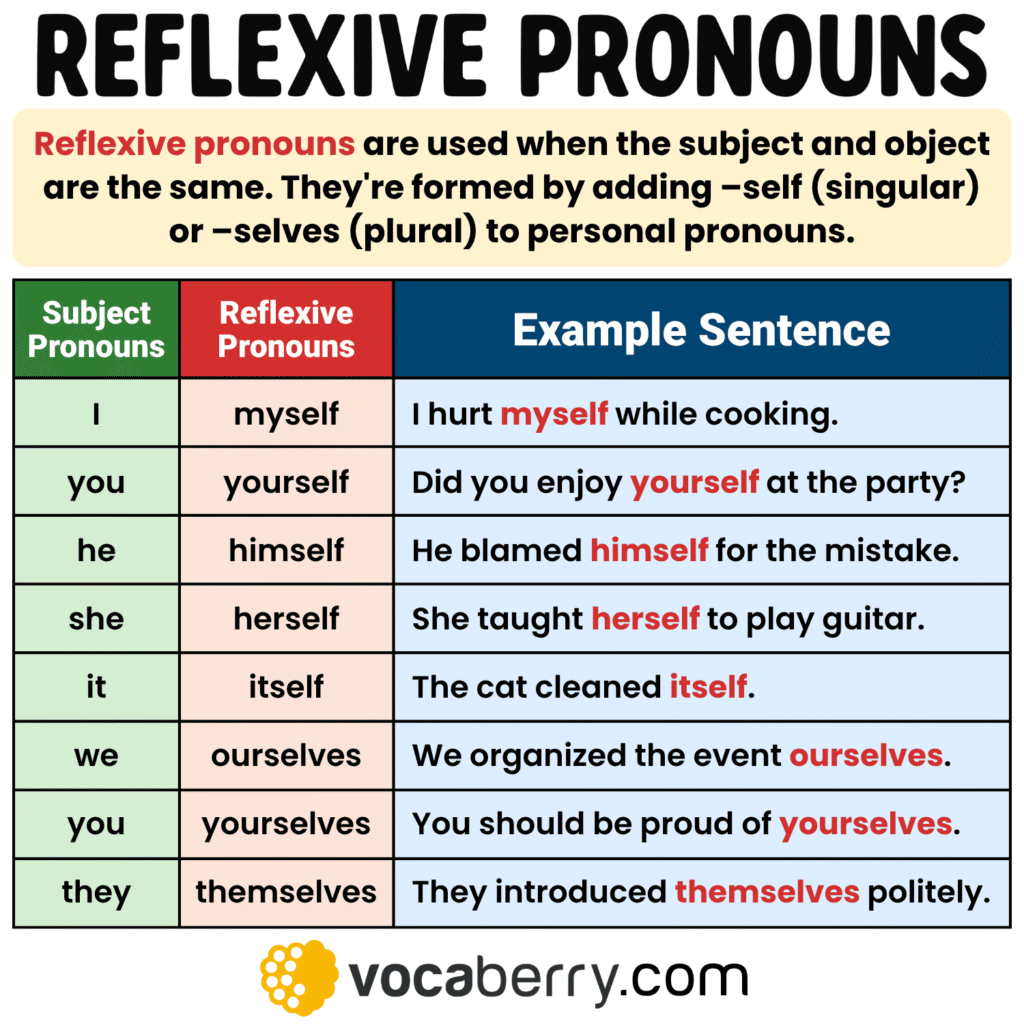
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and the object of a verb refer to the same person or thing. In other words, the person doing the action is also the one receiving it. These pronouns are formed by adding -self (for singular) or -selves (for plural) to personal pronouns. We use reflexive pronouns to show that someone does something to themselves, not to someone else.
List of Reflexive Pronouns with Examples
| Subject Pronoun | Reflexive Pronoun | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| I | myself | I hurt myself while cooking. |
| you (singular) | yourself | Did you enjoy yourself at the party? |
| he | himself | He blamed himself for the mistake. |
| she | herself | She taught herself to play guitar. |
| it | itself | The cat cleaned itself. |
| we | ourselves | We organized the event ourselves. |
| you (plural) | yourselves | You should be proud of yourselves. |
| they | themselves | They introduced themselves politely. |
How to Use Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and the object of a sentence are the same person or thing. They reflect the action of the verb back onto the subject. Here’s how and when to use them correctly in English grammar:
1. Same Subject and Object
Use a reflexive pronoun when someone does something to themselves.
Examples:
- I hurt myself while jogging.
- She looked at herself in the mirror.
- They introduced themselves at the meeting.
2. Reflexive Verbs
Some verbs are often followed by reflexive pronouns when the action is directed back at the subject.
Common examples include:
- blame – He blamed himself for the mistake.
- pride – She prides herself on her work.
- teach – I taught myself how to code.
- prepare – We prepared ourselves for the exam.
3. For Emphasis or Clarity
Reflexive pronouns can also be used to emphasize that someone did something without help or to stress who exactly performed the action.
Examples:
- I cleaned the entire house myself.
- The CEO herself approved the plan.
- He himself admitted the error.
Note: In these cases, reflexive pronouns act like intensive pronouns, though the form is the same.
4. After Prepositions
Sometimes, reflexive pronouns are used after prepositions to show that the subject is performing the action on themselves.
Examples:
- He was talking to himself.
- She bought a gift for herself.
- We kept it just between ourselves.
Position of Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns usually come immediately after the verb or after a preposition, depending on the sentence structure. Their position helps clarify that the subject and the object are the same person or thing. Here’s how their placement works:
1. After the Verb
Use a reflexive pronoun right after the verb when it acts as the direct object and the subject and object are the same.
Examples:
- I hurt myself during practice.
- She taught herself how to play the piano.
2. As an Indirect Object
Sometimes the reflexive pronoun acts as the indirect object, placed before the direct object.
Examples:
- He bought himself a new phone.
- We gave ourselves a break.
3. After Prepositions
When used with a preposition that refers back to the subject (e.g., for, to, by, with, about), the reflexive pronoun comes at the end of the prepositional phrase.
Examples:
- I made a sandwich for myself.
- She kept the truth to herself.
- He’s talking to himself again.
By + Reflexive Pronoun
The phrase by + reflexive pronoun is used to show that someone did something alone or without help. It emphasizes independence or isolation in the action.
Examples:
- She fixed the car by herself.
- He went to the concert by himself.
- The children made the cake by themselves.
- I enjoy spending time by myself on the weekends.
Reflexive Pronouns vs. Intensive Pronouns
Reflexive and intensive pronouns have the same forms (myself, yourself, himself, etc.) but serve different purposes in a sentence.
Reflexive Pronouns: Used when the subject and the object are the same. They are necessary to the sentence’s meaning. Examples:
- I taught myself to play the guitar.
- She looked at herself in the mirror.
Intensive Pronouns: Used only to emphasize the subject. They are not required for the sentence to make sense. Examples:
- I cooked dinner myself.
- The manager himself approved the request.
How to tell the difference?
- If you can remove the pronoun and the sentence is still correct → Intensive
- If you remove the pronoun and the meaning breaks → Reflexive
Reflexive Pronouns FAQs
What is a reflexive pronoun?
A reflexive pronoun refers back to the subject of the sentence and shows that the subject and object are the same person or thing. Example: She blamed herself for the mistake.
What are the 8 reflexive pronouns in English?
The 8 reflexive pronouns are: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves.
When should I use a reflexive pronoun?
Use a reflexive pronoun when the subject and object of the verb are the same. Example: I taught myself how to cook.
What is the difference between reflexive and intensive pronouns?
Reflexive pronouns are necessary to complete the meaning of the sentence. Intensive pronouns only add emphasis and can be removed. Example:
- Intensive: He himself finished the project.
- Reflexive: He hurt himself.
Can I use “myself” instead of “me”?
No, myself cannot replace me in regular subject-object situations. For example, it’s incorrect to say “Contact John or myself.” The correct form is “Contact John or me.”
Can reflexive pronouns come after prepositions?
Yes, if the preposition refers back to the subject. Example: She did it for herself.
Can reflexive pronouns be the subject of a sentence?
No, reflexive pronouns cannot function as the subject. They are always used as objects.
Are reflexive pronouns used for emphasis?
Yes, but when used this way, they are considered intensive pronouns. Example: I myself don’t believe it.
What is a common mistake with reflexive pronouns?
A common mistake is using a reflexive pronoun when it’s not needed. Example: “Myself will attend the meeting.” is incorrect; use “I will attend the meeting.”
Do reflexive pronouns change with verb tense?
No, reflexive pronouns remain the same regardless of verb tense. Only the verb changes. Example: She taught herself / She will teach herself.