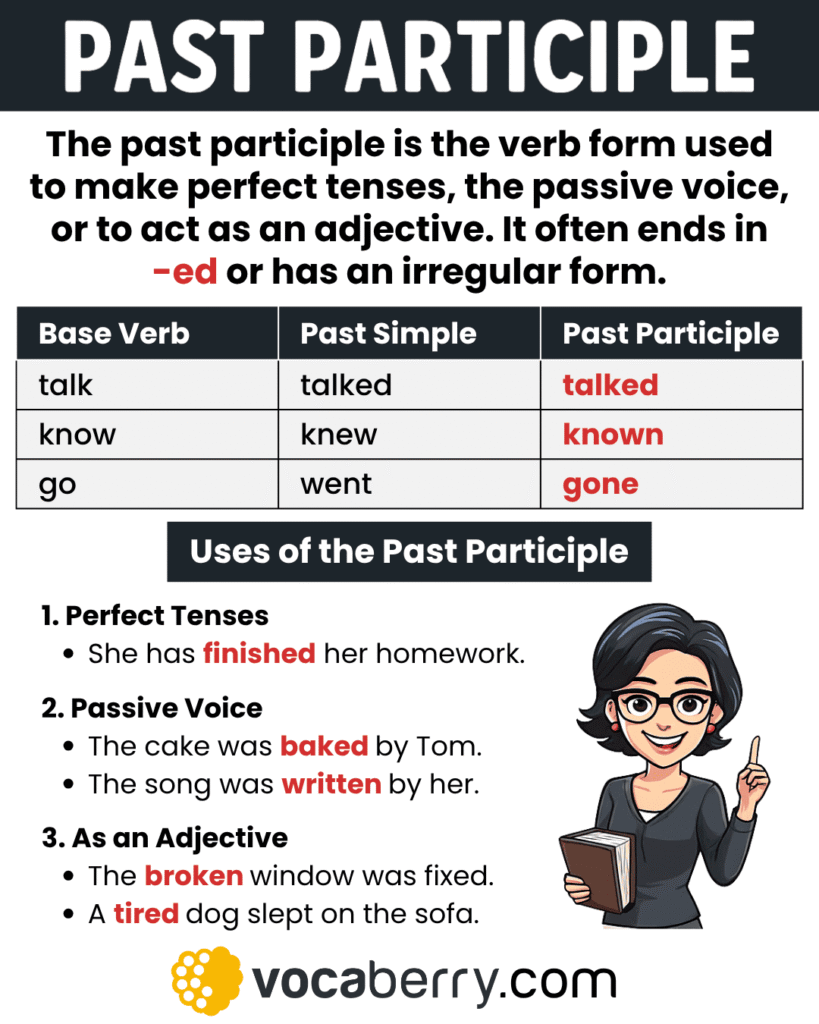
The past participle is the verb form used to create perfect tenses, the passive voice, and adjectives describing completed actions. Regular verbs form the past participle by adding -ed, while irregular verbs have unique forms that must be memorized. It often appears together with auxiliary verbs like have, has, had, or been.
In this article, you will find the definition, clear examples, spelling rules for forming the past participle, common uses in sentences, and a comparison with the past simple tense to help you use it accurately.
What Is the Past Participle?
The past participle is one of the main parts of a verb, used with auxiliary verbs like have, has, had, or be. It shows completed actions, forms the passive voice, and can function as an adjective. For regular verbs, it usually ends in -ed (e.g., played, watched), while irregular verbs have special forms that must be memorized (e.g., eaten, written).
| Infinitive | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| to be | was / were | been |
| to do | did | done |
| to go | went | gone |
| to take | took | taken |
| to write | wrote | written |
How to Form the Past Participle
The past participle form of a verb depends on whether the verb is regular or irregular.
1. Regular Verbs
For regular verbs, you form the past participle by adding -ed to the base verb.
| Base Verb | Past Participle | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| work | worked | She has worked here for years. |
| play | played | They have played all afternoon. |
| call | called | I’ve just called your number. |
| walk | walked | He has walked to school today. |
2. Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs have special forms for the past participle that do not follow regular spelling patterns. These forms must be memorized. Here are some common examples:
| Base Verb | Past Participle | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| go | gone | She has already gone home. |
| eat | eaten | He has eaten all the cake. |
| see | seen | I’ve never seen that movie. |
| write | written | She has written three books. |
Uses of the Past Participle
The past participle is very versatile in English grammar. It appears in several structures that describe actions, states, or qualities. Here are the main ways it is used:
1. Perfect Tenses
The past participle is used with have/has/had to form the perfect tenses. It shows that an action is completed relative to another time.
Examples:
- She has finished her homework.
- They had eaten before the guests arrived.
- I have seen that movie twice.
2. Passive Voice
The past participle combines with be (am, is, are, was, were, been) to show that the subject receives the action.
Examples:
- The cake was baked yesterday.
- These reports are written every week.
- The windows have been cleaned.
3. As an Adjective
Past participles can act as adjectives to describe nouns.
Examples:
- The broken window needs repair.
- The damaged goods were returned.
- The lost keys were found.
4. After Verbs of Perception and Causative Structures
In some structures, the past participle shows a completed action caused or perceived by someone.
Examples:
- I had my hair cut.
- She got the car fixed.
- We heard the song played on the radio.
5. Reduced Relative Clauses
When shortening relative clauses, the past participle describes the noun more concisely.
Examples:
- The documents signed yesterday are on your desk.
- The book written by the author won an award.
Spelling Rules for Past Participles
When forming the past participle, especially with regular verbs, there are important spelling rules to follow. These rules help you spell correctly and avoid common mistakes:
1. Verbs Ending in -e
If the verb ends in -e, simply add -d.
Examples:
- love → loved
- close → closed
2. Verbs Ending with Consonant + y
If the verb ends with a consonant + y, change y to i and add -ed.
Examples:
- carry → carried
- study → studied
3. One-Syllable Verbs Ending in Vowel + Consonant
If a one-syllable verb ends in a single vowel + consonant, double the final consonant before adding -ed.
Examples:
- stop → stopped
- plan → planned
4. Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs do not follow regular spelling patterns. You must memorize their past participle forms.
Examples:
- write → written
- choose → chosen
- eat → eaten
Irregular Past Participles with Examples
Here are common irregular verbs with their past participles and example sentences to help you learn and remember them:
| Base Verb | Past Simple | Past Participle | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| begin | began | begun | The meeting has begun. |
| break | broke | broken | She has broken her phone. |
| choose | chose | chosen | He has chosen a new career. |
| drink | drank | drunk | I have never drunk coffee. |
| drive | drove | driven | She has driven across the country. |
| eat | ate | eaten | They have already eaten lunch. |
| fall | fell | fallen | The leaves have fallen from the trees. |
| forget | forgot | forgotten | He has forgotten her birthday again. |
| go | went | gone | She has gone to the store. |
| see | saw | seen | I have seen that movie twice. |
| speak | spoke | spoken | He has spoken to the manager. |
| swim | swam | swum | She has swum across the lake. |
| take | took | taken | He has taken the keys with him. |
| wear | wore | worn | She has worn that dress before. |
| write | wrote | written | He has written three books. |
Past Participle vs. Past Simple
These two forms are commonly confused by English learners. Here’s how they differ:
Past Simple: The past simple is used alone to describe a completed action in the past. It does not require an auxiliary verb and is often used to tell when something happened.
- I saw the film yesterday.
Past Participle: The past participle is always used with an auxiliary verb like have or be. It shows a completed action that is connected to another time or can be used in the passive voice.
- I have seen the film.
- The film was seen by many people.
Conclusion
The past participle plays an important role in English grammar. It is used to form perfect tenses, the passive voice, and adjectives that describe nouns. When you understand how to create regular and irregular past participles, it becomes much easier to write accurately and fluently. Keep practicing with examples and reviewing common verbs so you can use past participles confidently in everyday English.