The present perfect tense is one of the essential tenses in English grammar, used to describe past actions that have a connection to the present. It is commonly used for life experiences, recent events, repeated actions, or situations that started in the past and continue now. The structure combines have/has + past participle, making it important for expressing both completion and ongoing relevance.
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to use the present perfect tense in affirmative and negative forms, make present perfect questions, understand its verb structure and usage, review essential grammar rules, and explore common time expressions—with clear examples.
When to Use the Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense is used to describe past actions that affect the present. It’s ideal when the exact time isn’t important, and the focus is on results, experiences, or ongoing situations. This tense is often used with expressions like “already, yet, just, for, and since” to show relevance or continuity.
1. Life Experiences
Used to describe things someone has done at any time in their life, without saying when.
- I have visited Japan three times.
- She has tried sushi before.
- Have you ever seen a whale?
2. Actions Completed Recently (Just, Already, Yet)
Used for actions that have happened in the near past and may still be important or relevant now.
- I have just finished my homework.
- He has already left the office.
- Have you eaten yet?
3. Unfinished Actions (For, Since)
Used to describe actions or states that started in the past and are still continuing in the present.
- We have lived in this house for ten years.
- She has worked here since 2015.
- They have been married for a long time.
4. Past Actions with Present Results
Used when a past action affects the current moment, even if the time isn’t mentioned.
- Someone has broken the window!
- I’ve lost my keys—I can’t get in.
- He has cut his finger. Look!
5. Multiple or Repeated Past Actions
Used to describe actions that have happened several times up to now.
- I have read that book many times.
- We’ve visited London every summer.
- She has called him five times today.
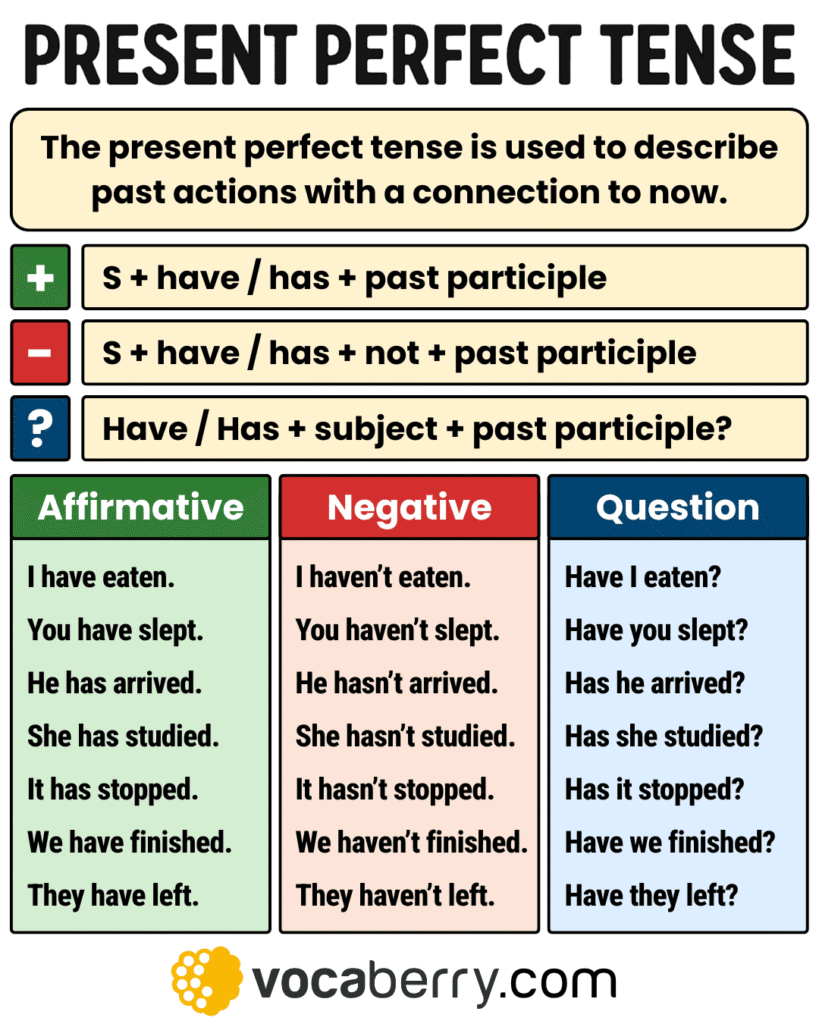
Present Perfect Tense Structure
The present perfect tense is formed with two parts: the auxiliary verb “have” or “has” and the past participle (also known as the third form of the verb). It has several uses—affirmative statements, negative sentences, and questions—all following a consistent pattern.
Affirmative Form
Use this form to state actions or experiences with relevance to the present.
Structure: Subject + have/has + past participle
Examples:
- I have finished my homework.
- She has visited Spain twice.
- We have known each other since school.
Negative Form
Use this to show that something has not happened yet or hasn’t occurred at all.
Structure: Subject + haven’t/hasn’t + past participle
Examples:
- I haven’t seen that film yet.
- He hasn’t called back.
- They haven’t decided on a date.
Question Form
Use this to ask whether an action has taken place.
Structure: Have/Has + subject + past participle?
Examples:
- Have you read the book?
- Has she arrived already?
- Have they finished working?
Short Answers
In conversational English, responses to yes/no questions are short and direct.
Examples:
- Have you eaten? → Yes, I have. / No, I haven’t.
- Has he called? → Yes, he has. / No, he hasn’t.
- Have we started? → Yes, we have. / No, we haven’t.
Summary Table
| Type | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | S + have/has + past participle | She has studied French. |
| Negative | S + haven’t/hasn’t + past participle | I haven’t finished the report. |
| Question | Have/Has + S + past participle? | Have they left yet? |
| Short Answer | Yes/No + S + have/has | Yes, she has. / No, he hasn’t. |
Time Expressions with the Present Perfect Tense
Here are the most common time expressions used with the present perfect tense. These words and phrases help show how recent, how often, or how long something has happened in connection with the present. They typically signal completion, life experience, or ongoing relevance—key aspects of how the present perfect is used.
| Time Expression | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| already | She has already finished her homework. |
| yet | Have you eaten yet or are you still hungry? |
| just | I have just seen that new action movie. |
| ever | Have you ever been to Paris in spring? |
| never | I have never tried sushi before. |
| for | We have lived here for almost five years. |
| since | He has worked at this company since 2015. |
Past Participles in Present Perfect Tense
In the present perfect tense, the main verb always appears in its past participle form. This form is used with have/has to describe actions that have been completed at some point in the past but still relate to the present moment. There are two types of past participles: regular and irregular.
Regular Past Participles
Most verbs form the past participle by simply adding -ed to the base verb:
| Base Verb | Past Participle | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| work | worked | She has worked at the same office for five years. |
| play | played | We have played board games every Friday night. |
| watch | watched | He has watched that documentary multiple times. |
| clean | cleaned | I have cleaned the entire house this morning. |
| talk | talked | They have talked about moving to another city. |
| study | studied | She has studied Spanish for more than two years. |
Irregular Past Participles
Irregular verbs do not follow the regular -ed pattern. You must memorize their past participle forms:
| Base Verb | Past Participle | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| go | gone | She has gone to the store near the train station. |
| eat | eaten | I have eaten sushi at that place several times. |
| write | written | He has written three novels in the last decade. |
| see | seen | Have you seen the new art exhibit downtown? |
| take | taken | They have taken the exam two times already. |
| break | broken | We have broken two glasses in the last few days. |