The future perfect tense is used to describe actions or events that will be completed before a specific time in the future. It shows that something will already be finished by a certain deadline. This tense often describes future accomplishments, expectations, or plans that must be completed before another future moment. The structure combines will + have + the past participle, showing the action will be complete before a certain point in time.
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to form and use the future perfect tense in affirmative, negative, and question forms, understand its structure, grammar rules, and usage, explore common time expressions, and see clear examples.
When to Use the Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is used in English to show that an action will be completed before a specific time or another action in the future. It helps you clearly express deadlines, expectations, and the idea that something will already be done at a certain point. Below are the most common ways you use this tense:
1. To Show Completion Before a Specific Time in the Future
Use it to say something will finish before a future moment or date.
Examples:
- She will have graduated by next June.
- By 8 o’clock tonight, I will have prepared the presentation.
- They will have built the new library by the end of the year.
2. To Indicate Completion Before Another Future Action
Use it when one future action happens before another action starts.
Examples:
- I will have cleaned the house before the guests arrive.
- He will have left for work before you wake up.
- We will have eaten dinner by the time they get here.
3. To Make Assumptions or Predictions About the Past
Use it to express an expectation that something will have already happened, based on what you know.
Examples:
- She will have reached the station by now.
- He will have finished the report before the meeting starts.
- They will have heard the news by tomorrow morning.
Future Perfect Tense Structure
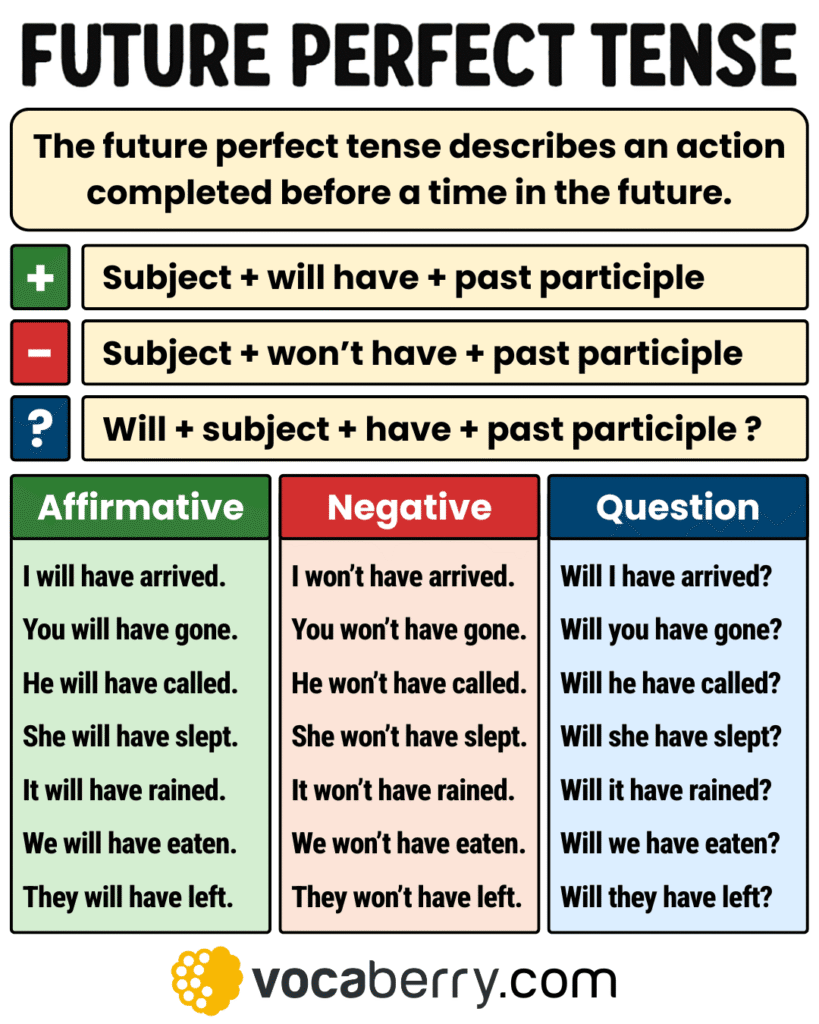
The future perfect tense is formed by combining will + have + the past participle of the main verb. This structure stays the same for all subjects and is used in affirmative statements, negative sentences, questions, and short answers. It shows that something will be completed before a certain time or another event in the future.
Below, you’ll learn how to form each type with clear examples:
Affirmative Form
Use this form to say that something will be finished by a specific time.
Structure: Subject + will have + past participle
Examples:
- She will have finished the report by Friday.
- They will have left before you arrive.
- I will have completed the course by next month.
Negative Form
Use this form to say that something will not be completed by a certain point in the future.
Structure: Subject + will not (won’t) have + past participle
Examples:
- He won’t have read the book before the meeting.
- We will not have cleaned the house by noon.
- You won’t have saved enough money by December.
Question Form
Use this form to ask whether something will be finished by a specific future time.
Structure: Will + subject + have + past participle?
Examples:
- Will she have cooked dinner by 7 o’clock?
- Will they have finished the project before the deadline?
- Will you have graduated by next year?
Short Answers
Use short answers for yes/no questions.
Examples:
- Will you have finished the project? – Yes, I will. / No, I won’t.
- Will he have arrived at the airport? – Yes, he will. / No, he won’t.
- Will they have left the office? – Yes, they will. / No, they won’t.
Summary Table: Future Perfect Tense
| Type | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | S + will have + past participle | She will have finished her homework. |
| Negative | S + will not have + past participle | They won’t have arrived by 6 p.m. |
| Question | Will + S + have + past participle? | Will you have completed the work by Friday? |
| Short Answer | Yes/No + S + will/won’t | Yes, I will. / No, I won’t. |
Regular and Irregular Past Participles
In the future perfect tense, you must use the past participle form of the main verb after will have. This form shows that the action will be fully completed before a specific time in the future. There are two types of past participles you need to know: regular and irregular.
Regular Past Participles
For regular verbs, the past participle is formed by simply adding -ed to the base verb.
| Base Verb | Past Participle | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| finish | finished | She will have finished the report by tomorrow. |
| clean | cleaned | They will have cleaned the house before guests arrive. |
| watch | watched | He will have watched all the episodes by then. |
| call | called | I will have called you by the end of the day. |
| paint | painted | We will have painted the room by Saturday. |
| work | worked | She will have worked here for ten years by next month. |
Irregular Past Participles
Irregular verbs do not follow the -ed pattern, so you need to memorize them. Here are some of the most common irregular past participles:
| Base Verb | Past Participle | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| go | gone | She will have gone to the airport before noon. |
| see | seen | They will have seen the movie already. |
| take | taken | He will have taken the exam by next week. |
| write | written | I will have written the report before Friday. |
| eat | eaten | We will have eaten dinner by 8 o’clock. |
| begin | begun | She will have begun her new job by March. |
Time Expressions with the Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is often used with time expressions that show a deadline or point in the future by which an action will be completed. These expressions help clarify when something will already be finished relative to another time or event. Time expressions can refer to a specific point (e.g., by 5 p.m.), a period (e.g., in two days), or another action (e.g., by the time you arrive).
Here are the most common time expressions and examples of how they’re used:
| Time Expression | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| by tomorrow | She will have finished the report by tomorrow. |
| by next week | They will have moved into their new house by next week. |
| before | He will have left before you arrive. |
| by the time + clause | By the time you get home, I will have cooked dinner. |
| in two days | I will have completed the project in two days. |
| within a week | I will have finished reading the book within a week. |
| by the end of the year | We will have saved enough money by the end of the year. |
| before then | She will have finished her assignment before then. |
| by that time | They will have completed the repairs by that time. |
| by then | I will have left the office by then. |
| by 5 p.m. | She will have submitted the application by 5 p.m. |