
The simple present tense is one of the most commonly used tenses in English grammar. It describes actions that happen regularly, facts that are always true, and situations that are fixed or scheduled. This tense is essential for talking about daily routines, habits, scientific facts, instructions, and timetables.
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to use the simple present in positive and negative sentences, form questions, understand its structure, and apply third-person verb rules—all with clear examples.
When to Use the Simple Present Tense
The simple present tense is used to describe actions, situations, or facts that are regular, general, or always true. It covers a range of uses such as stating facts, habits, routines, scheduled events, and instructions. Each use depends on context, but the structure remains consistent.
1. General Truths & Facts
Used when stating objective facts or scientific truths:
- Water boils at 100 °C.
- The earth revolves around the sun.
- A week has seven days.
2. Habits & Daily Routines
Describes actions regularly occurring:
- I wake up at 6 a.m. every day.
- She takes the bus to school.
- They eat dinner together each night.
3. Scheduled Events & Timetables
Used for planned events in the future (especially with public schedules):
- The train leaves at 8 p.m.
- The store opens at 9 a.m. every Monday.
4. Permanent Situations & Lasting Conditions
Describes long-term truths, lifestyles, or locations:
- He works as a teacher.
- They live in Spain.
- That store sells furniture.
5. Instructions, Directions & Commentary
Common in guides, recipes, or broadcasting:
- First, turn left at the traffic light.
- Add two cups of flour.
- Smith passes to Adams, Adams shoots—he scores!
6. Stative Verbs
The Simple Present also works with stative verbs. These verbs typically aren’t used in continuous forms (e.g., “I know” not “I am knowing”).
- She knows the answer.
- I believe you.
- He smells smoke.
Simple Present Tense Structure
The Simple Present Tense has a fixed structure that changes based on sentence type: affirmative, negative, or question. It also depends on the subject—especially when using he, she, or it (third person singular). The base form of the verb is used, with -s or -es added in some cases, and do/does used for negatives and questions.
Affirmative Form
To form a positive sentence in the simple present, use the base form of the verb. For he, she, it, add -s or -es to the verb.
Subject + base verb (add -s or -es for he/she/it)
| Verb Ending | Third Person Singular | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| most verbs | add –s | work → works, run → runs |
| -ch/-sh/-x/-ss/-o | add –es | go → goes, watch → watches |
| consonant + y | y → ies | study → studies |
| have | has | have → has |
Examples:
- I walk to school.
- She plays the piano.
- It rains a lot here.
Negative Form
For negative sentences, use do not (don’t) or does not (doesn’t) + the base verb. Don’t add -s to the verb, even for he/she/it.
Subject + do/does + not + base verb
Examples:
- I don’t eat meat.
- He doesn’t watch TV.
- They don’t like cold weather.
Question Form
To form questions, start with do or does, then add the subject and the base verb. Use does for he/she/it.
Do/Does + subject + base verb?
Examples:
- Do you play football?
- Does she work here?
- Do they live nearby?
Short Answers
Use “do/does” for yes or no replies. These are common in spoken English.
Examples:
- Yes, I do. / No, I don’t.
- Yes, he does. / No, he doesn’t.
Summary Table
| Type | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | S + V / V‑s/es | He reads the newspaper every morning. |
| Negative | S + do/does + not + V | They don’t watch TV on weekdays. |
| Question | Do/Does + S + V? | Does she play guitar? |
| Short Answer | Yes/No + S + do/does | Yes, she does. / No, they don’t. |
Time Expressions in the Simple Present Tense
The simple present tense is often used with specific time expressions that show how often something happens. These words and phrases help clarify whether an action is habitual, repeated, or part of a routine.
Time expressions in the simple present usually answer the question:
“How often?”, “When?”, or “On which days?”
Common Time Adverbs
These words describe frequency — how often something happens:
| Adverb | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| always | She always drinks tea in the morning. |
| usually | I usually walk to work. |
| often | They often go hiking. |
| sometimes | We sometimes eat out on Fridays. |
| rarely | He rarely watches TV. |
| never | She never eats fast food. |
Regular Time Phrases
These phrases talk about routines tied to specific times or days:
| Time Phrase | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| every day | He runs every day. |
| every week | They meet every week. |
| on Mondays | I clean the house on Mondays. |
| in the morning | She reads in the morning. |
| at night | We study at night. |
| once a week | He visits his grandparents once a week. |
| twice a month | I go to the dentist twice a month. |

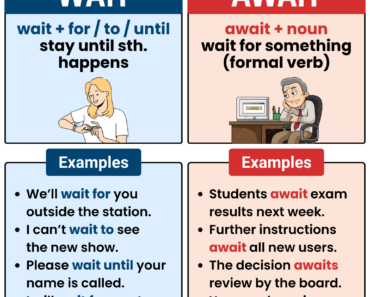





hi the person who wriite this is so intellgent i am so appresiate and also people who want learn english are also happy when the see your grammar
it is very good explanation